INCOME TAX RULES
INCOME TAX RULES FOR FOREIGN NATIONALS IN INDIA

According to the Income tax act, 1961, all the income (from any source) which is earned and received in India by selling goods or service or by way of employment is taxable as per Indian Income tax rules.
Every country has different Income taxation rules, accordingly India opted for "Residency based taxation" rather than "citizenship based taxation". Depending on the type of income a foreign national has earned, will decide the process of Income tax which is to be applied.
1. Employment Income: It can be in cash/kind that is received out of an individual's employment in some organisation. Salaries/Wages, bonus, cash compensation, commission, perquisites, allowances etc. are included in the employment Income.
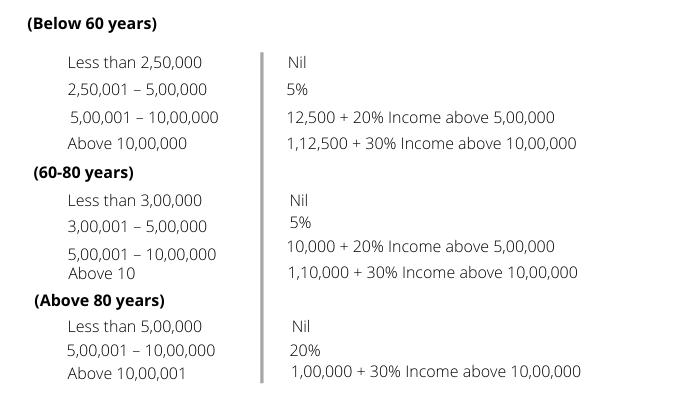
However, in the recent finance bill 2020, certain amendments in the direct tax are introduced which gives every taxpayer the option to choose whether to go for certain exemption/deduction or to choose a different set of income tax slab rate which is:

2. Non-Employment Income: It includes certain long & short term capital gains earned on the disposal of capital assets situated in India or any kind of royalty received. Long-term capital (LTC) gains taxed at a flat 20%. Short term capital (STC) gains taxed at 15%, (if listed). Royalties/Interest earned from an Indian entity, they are taxable at 10%.
- Income from investment abroad but send to bank account in India
- Sale of assets in India
- Interest payments on infrastructure debt funds
Related Blog: TAX AUDIT LIMIT FOR BUSINESS/PROFESSION IN INDIA
3. Other Income taxes: A surcharge of 12% of the tax for taxpayers whose Income is more than 1 Crore & 3% education cess. Additionally foreign national will also have to contribute for the social security scheme in force.
There are various situations where foreign nationals are worried for the multiplicity in Income tax because of the mismatch in their residential status and the country in which they have earned that income. There arises a situation of double taxation. To boost the morale of foreign nationals and allow them to render services freely in any part of the country, Government of India has signed several Double taxation avoidance agreements (DTAA) with more than 90 countries.
Double taxation avoidance agreements (DTAA): DTAA is a tax treaty between two or more countries to avoid taxation of the same income twice. When a taxpayer resides in one country and earns a considerable amount of income in another country, there arises the need for DTAA. A foreign taxpayer who is working in India would be able to reduce taxable income in their country of primary residence under a double taxation avoidance agreement.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED BY FOREIGN NATIONALS
More or less the documents which are required to be submitted while filing income tax are the same whether you are a resident or a foreign national, but there are certain other formalities for foreign nationals or expatriates.
- Form 16: This is an informative form which is provided by the employer and it contains the information regarding an individual's income and any deductions thereof, throughout the financial year.
- Form 16A (TDS certificate): It specifies the TDS & nature of such payment which is being deposited to the income tax department throughout the year by the taxpayer.
- Bank Statements/Passbook: Expats/Foreign nationals are required to give bank statements demonstrating all exchanges made in the span of the tax collection period.
- Property details: Any property sold within India will attract a capital gains tax on compensation from the deal. Insights about the same of any property in India must be specified while documenting Income Tax Returns.
- Proof of Investment: Investment which does not form part of your Form 16 which is provided to you by your employer must be specified separately along with the proofs stating your investment.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
Q Who is considered as a foreign national in India?
Ans: Any individual who is residing and working in India but belongs to any other country is considered as foreign nationals.
Q Are foreign nationals liable to pay tax in India?
Ans: Yes, all the foreign nationals are liable to pay tax in India under the income tax act, 1961. But the provisions for their taxation are different from that of an Indian citizen.
Q Are foreign nationals liable to pay tax on capital gains in India?
Ans: Yes, foreign nationals are liable to pay taxes on capital gains when they sell any capital asset within India.
Q Can a foreign national file an income tax return?
Ans:Yes, foreign nationals are also required to file an income tax return in India by abiding various rules and regulations stated in taxation laws of India.
